
Pianos that could play back music from a punched paper roll, ie a pianola were once quite common. Playing a stringed instrument mechanically is rather more complicated. The general term for a machine that plays more than one kind of instrument is an Orchestrion. They were controlled by either perforated paper rolls or pin barrels. More info came be found here. The players were often coin-operated, and were placed in ice cream parlours, billiard halls, restaurants, dance halls, theatres, and so on.
The timing of the introduction of these machines, around 1907-1912 seems a little odd; according to Wikipedia, disc recordings were popular and had almost completely superseded wax cylinders by 1912. The reason is probably that disc reproduction then was so poor that real instruments would sound very much superior. No problems with intermodulation distortion!

THE SANDELL SELF-PLAYING VIOLIN PATENT
 |
| Left: The Sandell Patent: 1907
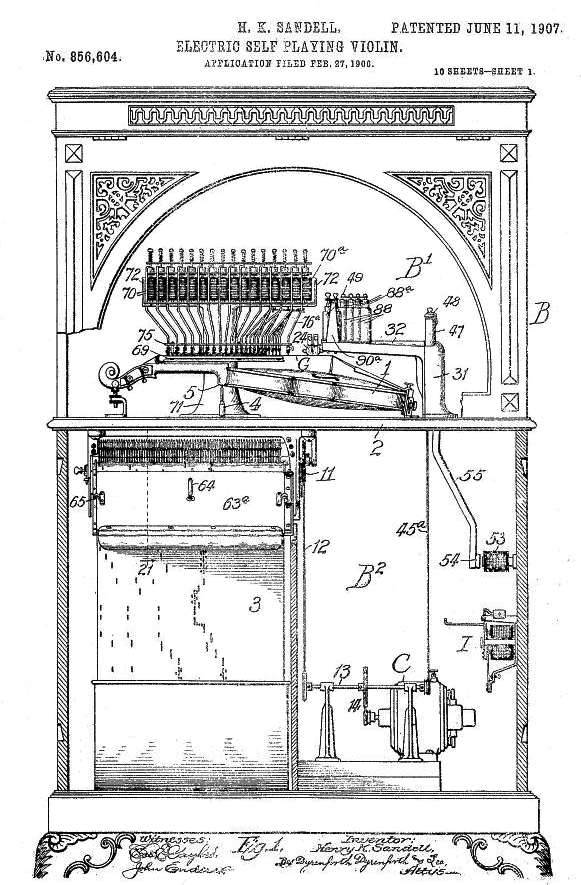
This machine was wholly electric, with the stopping of the strings controlled by a bank of solenoids. (70) These were controlled by contacts pressing against the paper roll; when there was hole in the paper the contact touched an electrified bar and the appropriate solenoid was energised.
The strings were bowed by four rosin-coated friction wheels 24; these could be pressed harder against the string by more solenoids, (88) to give dynamics, ie a louder or softer sound. These wheels were turned by the electric motor C which also moved the paper roll. There is no integral piano.
This is a complicated patent that runs to 20 pages. Everything looks well worked out, strongly suggesting a working model had already been built. It claims to "improve, in matters of detail, the self-playing musical string-instrument which forms the subject of Letters Patent of the United States No. 807,871, dated December 19, 1905"
The patent was assigned to the Mills Novelty Company of Chicago; see below.
US Patent 856,604. June 1907
|
 |
| Left: The Sandell Patent: 1907
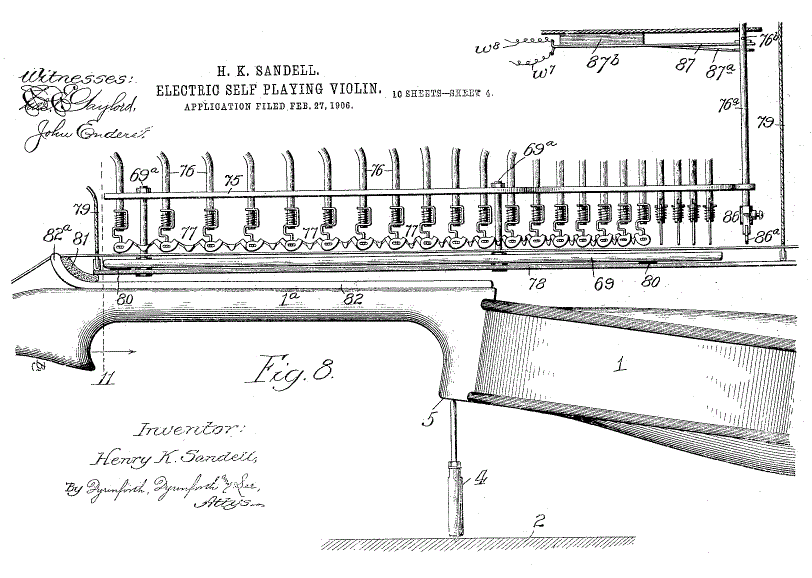
This shows the plungers for stopping the strings. The rods 76 running upwards were depressed by a bank of solenoids 70, guided by holes in the cover-plate 75. Four picker-fingers 86 were provided to allow the strings to be plucked rather than bowed, ie Pizzicato, and were operated by solenoids such as 87b.
The violin 1 is partially supported by the jackscrew 4.
US Patent 856,604. June 1907
|
 |
| Left: The Sandell Patent: 1907
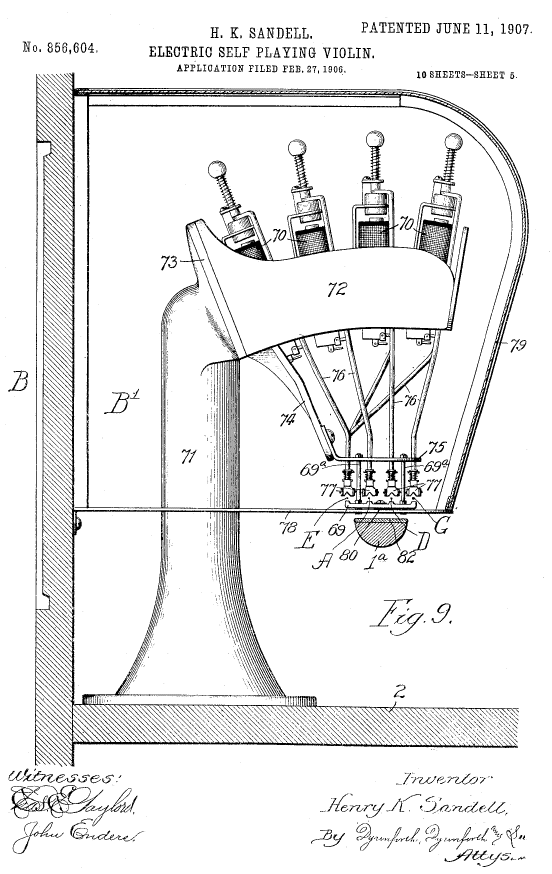
This is an end-on view along the axis of the violin neck 1a. The support 71, 72 holds the solenoids 70 above the violin.
US Patent 856,604. June 1907
|

THE WAUTERS AUTOMATIC VIOLIN
 |
| Left: The Wauters Automatic Violin: 1907
More competition for the Hupfeld.
This is an article in Scientific American about the Wauters Automatic violin:
An Automatic Violin Player: By George Gilbert on 28 December 1907
"In view of the present popularity of the piano player, and the marvelous perfection this instrument has attained in reproducing the work of the best musicians, it is very evident that it will be only a question of time before other musical instruments must similarly surrender to mechanical control. The latest development along this line is a machine which will play violins and kindred instruments. As may well be imagined, the violin offers difficulties which are peculiar to itself, and we are not surprised to learn that the Violin player illustrated herewith is the culmination of seven years of continuous labor and experiment."
"The instrument requires no alteration in the violin itself, and any violin may be placed in the player and removed without injury. The parts are pneumatically controlled in a manner similar to that of the ordinary piano player. A perforated music sheet selects the notes which are to be sounded. This sheet travels over a "tracker board," provided with the usual ducts in which an exhaust is maintained. There are two ducts for each note, and as these are uncovered by perforations in the music sheet, the air rushing into one of the ducts acts through the medium of the usual valves and pneumatics to press a finger down on one of the violin strings at the proper point on the finger board, while the air in the other duct puts into operation the bowing mechanism of this string. The bowing is done by means of four crystal disks, one for each string."
|
|
 |
| Left: The Wauters Automatic violin: 1907
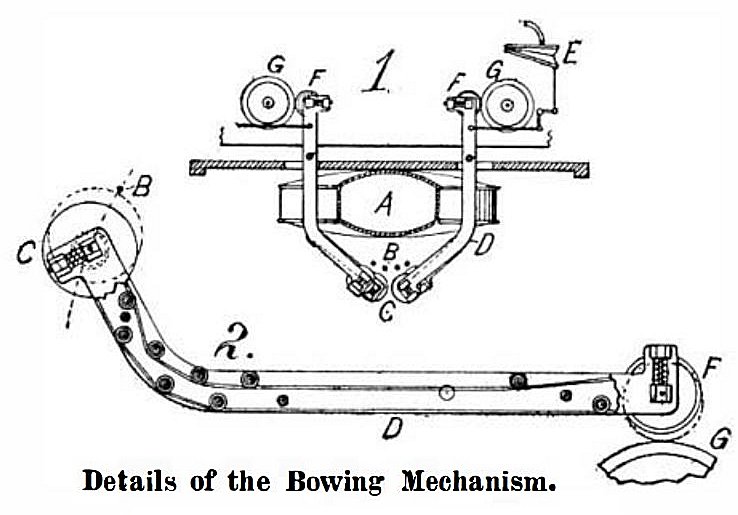
"In the accompanying drawing the details of the bowing mechanism are shown. Fig. 1 illustrates a section taken through the body of the violin A., The strings are indicated at B. The disks G, with which the bowing is done, are an inch in diameter and % of an inch in thickness. They are mounted in the ends of levers D, which are connected to the pneumatics E. When one of the bow ducts is uncovered, it operates a valve, which connects its respective pneumatic E with the exhaust chamber of the machine. The pneumatic is thus deflated, swinging the lever D to which it is connected, and bringing the disk G on this lever into contact with the selected string B."
"The disk G is rotated at high speed by means of a belt, which is guided along the lever D, as best shown in Fig. 2, and runs over a pulley F at the opposite end of the lever. When the lever D is swung into operative position by the pneumatic E, the pulley F is brought into contact with a driving pulley G, and is set in motion by a frictional contact therewith. This motion is communicated to the disk G, which operates on the violin string."
|
|
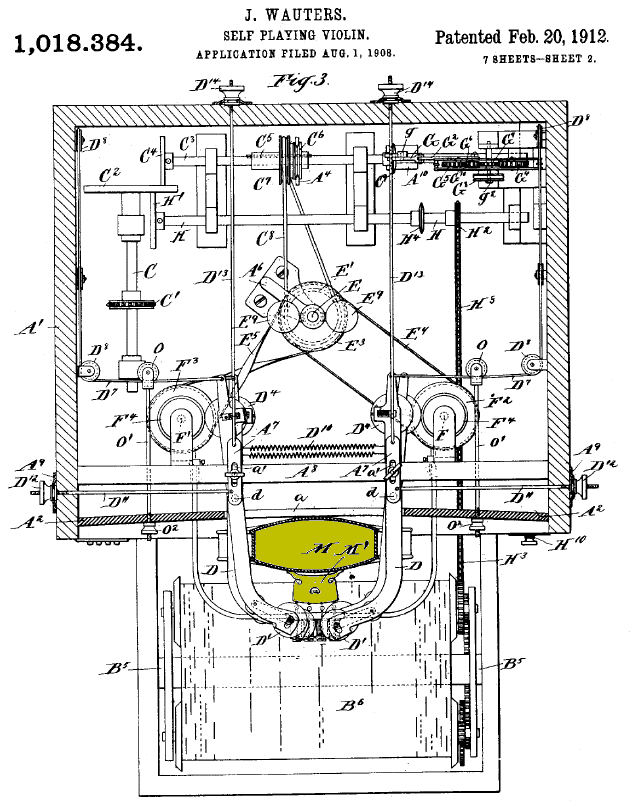 |
| Left: The Wauters Automatic violin patent: 1912
This top-view drawing from Wauters' patent shows the complexity of the machine; the violin is shaded. The drums holding the perforated music sheet are at the bottom of the image.
"The speed of revolution may run up as high as 2,000 revolutions per minute. The rate at which the disks revolve determines the loudness of the tones. A device is provided for applying rosin to the disks. This consists of a small cup attached to a spring arm and containing rosin, which bears against the revolving disks."
"The fingers of the violin player are sixty-five in number, although more can be added if desired, to reach the extreme high range of the A and E strings. There is a finger for each note. The model shown employs fingers reaching the seventh position. In front of each string is stretched a rubber band, upon which the ends of the fingers strike, thus producing a touch like that of the human finger, and making it possible to imitate the "slide." The tremolo is produced by a set of four hammers, which are actuated by electric vibrators of the type used in call bells. When a hammer vibrates against, a string, next to the bridge, the tremolo effect. is produced on that string. All the strings may have this effect, or one, as the character of the music demands." (I think he meant vibrato, a cyclic variation in pitch. Tremolo is a cyclic variation in volume: ED)
"Directly over the violin are four small pitch pipes, which are blown, on pressing a button, by causing air to pass through the pipes, each of which gives the tone of one of the strings, G, D, A, or E. The operator then tunes the violin in unison with the pitch pipes. Violinists know that it is hard to keep a violin in tune. But few appreciate that this is due to the sweat of the player's fingers, which makes the strings stretch. Strings on instruments placed in the violin player do not need much tuning. Silk E strings have been found to last two months, and have stayed in tune two weeks without attention."
|
|
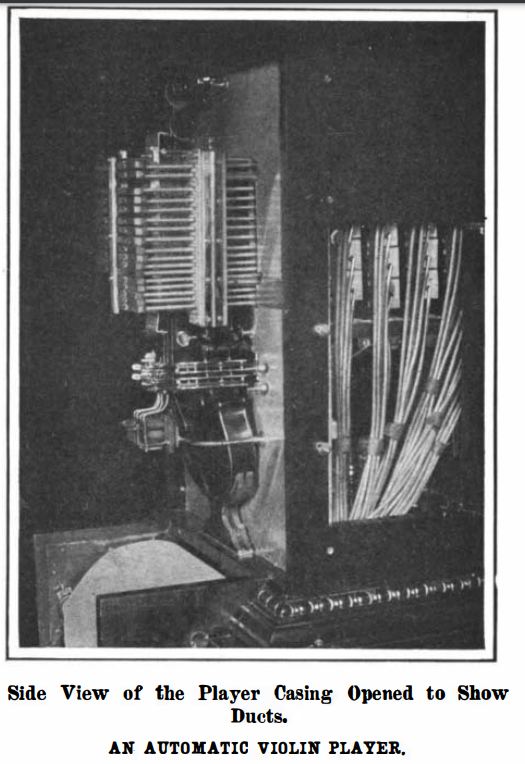 |
| Left: The Wauters Automatic violin: 1907
"The tempo is varied by means of a friction pinion which is moved radially on the face of a large driving wheel. This device for varying the tempo enables the simulation of rubato passages when it is operated by a skilled musician. Instruments of the violin family have four strings, each with a range of two octaves. The violin player enables each string to be treated, at will, as a separate violin, as each bow is controlled by a separate mechanism. In the model shown, the higher portions of the G and D strings are not utilized, but they can be by supplying extra fingers. Notes on a violin are found sometimes on each of the four strings. For instance, the G above the treble staff may be struck on all the strings; so that if a trill were being performed on that note on one string, an arpeggio passage containing the same note could be produced on the other strings. Of course, no human player could do that."
"It is possible for the player to render a solo part, with a cello accompaniment on the bass strings, or a solo with two accompanying violin parts, all on one violin. The possibilities for combinations of orchestral effect, therefore, are seen to be many. Harmonics are produced by the application of just enough pressure to a finger to make it rest lightly in the string sounded, thus imitating the action of the human finger. Trills are produced with striking clearness by providing a series of small perforations in the music roll. The same principle applied to the bow pneumatics produces springing bow and flying staccato. In making the first music rolls for the player, the inventor, Prof. Wauters, of Binghamton, N. Y., had many technical details to solve. Instruments having fixed strings or tones are played on the tempered scale. But violins play on the untempered chromatic scale, and therefore it was necessary for Prof. Wauters to lay the groundwork for producing music rolls for instruments of that character."
|
This shows the bundles of piping leading to the fingering pneumatics. (bellows)
|

THE HUPFELD PHONOLISZT VIOLINA
 |
| Left: The Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina; mechanical playing of three violins and pianola: 1912
According to Antique HQ, the Hupfeld company “sold this type of instrument for 20 years without any competitors”; as you can see from the rest of this page, the statement about having no competitors appears to not be true. It would be good to know how many were actually sold.
The instrument was manufactured by Ludwig Hupfeld at Leipzig, Germany.
Source: Popular Mechanics for Mar 1912, p424
|
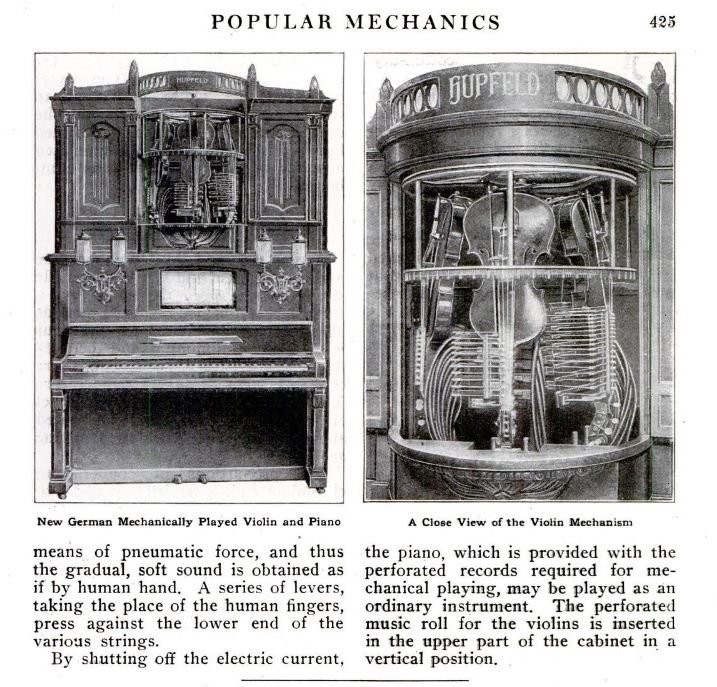 |
| Left: The Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
The machine is electrically powered, but the stoppng of the violin strings is pneumatic (and so is the pianola section) so there was an electric compressor to provide air pressure. Some pianola were worked by vacuum rather than pressure (see the pianola page) but in that case the working pressure differential cannot exceed 1 Bar. However you can use as much pressure as you like, which is probably helpful when designing a large and complicated machine.
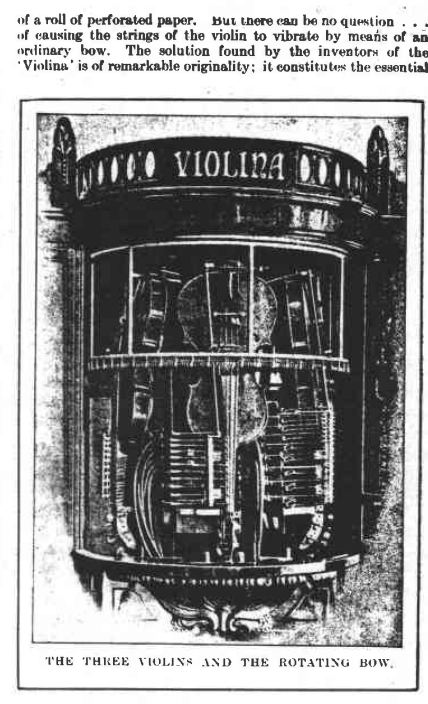
The three violins were bowed by by a circular structure carrying 1300 horsehair threads which can be seen running across the narrowest part of the violin body. This, the vertical columns, and the upper circle all rotate as one unit.
You might think that it would be a continual labour to keep the three violins in tune- with a total of twelve strings to adjust- but it appears to have been a manageable business. I consulted a violinist who confirmed that sweat from the player's fingers on the strings is a major source of violins going out of tune; that of course was not a factor here. Nonetheless you would have thought that thermal expansion alone would require some attention to the tuning. Another point that has just come to light is that only one string on each violin was actually played, so you only had three strings to keep tuned.
Source: Popular Mechanics for Mar 1912, p424
|
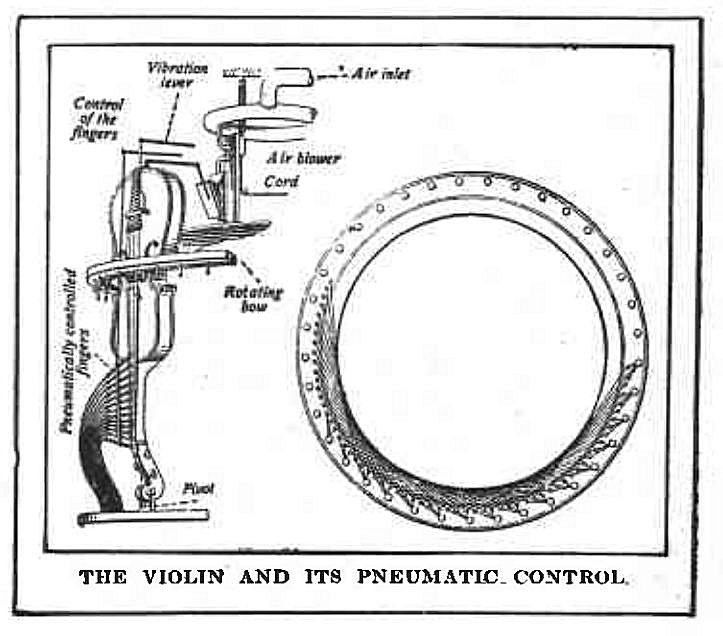 |
| Left: Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 2008
This shows how the initially puzzling circular bow worked; it was in fact made up of a series of straight lines that approximated a circle.
It was made up of 1350 horsehair strands.
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
Source: Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
Source: Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
This confirms that the Violina worked on compressed air, and not vacuum.
Source: Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
A close-up of the three violins.
Source: Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
Source: Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Article on the Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina: 1912
Source: The Literary Digest; original source article by A. Troller in La Nature 8 June 1912, Paris
|
 |
| Left: Hupfeld Phonoliszt Violina restored: 2008
The machine has been restored to its original condition by Dutch restorer Fred Bernouw. Its current location has not been discovered.
Source: Classic FM, which page includes two videos of the machine in action. It is claimed that the second recording (a Chopin piece) clearly demonstrates the machine can even do vibrato, but looking at the string-stoppers I reckon its more of a trill.
|
A Hupfeld sold for US$ 658,000 at Bonhams in October 2010. You can read about its history here.
The Hupfeld machine was described in the magazine Music Box, summer 1970 edition.
At least one Hupfeld machine was built that played six violins. It is in Siegfried's Mechanical Music Museum at Rüdesheim, Germany.

THE MILLS VIOLANO VIRTUOSO
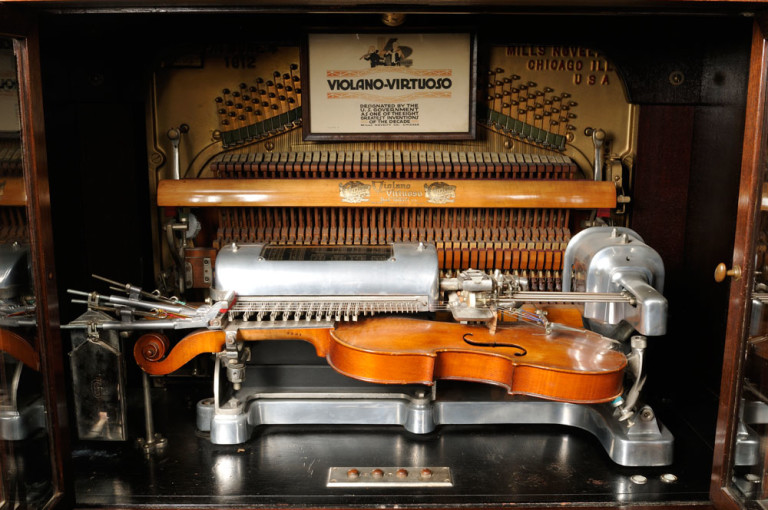 |
| Left: Mills Violano Virtuoso: 1911
Hupfeld was not without competition. This combined piano and single violin player was made by the Mills Novelty Company in the 1920s. The strings were bowed by a number of wheels so more than one string could sound at once.
You can see it on YouTube.
|
An anonymous someone wrote a book on the Mills Violano Virtuoso; see here, claiming it was the "World's Only Self-Playing Violin And Piano" which at the time it was written (1900 is stated, but that sounds a bit early) may have been true.
There's a Violano Virtuoso for sale here.
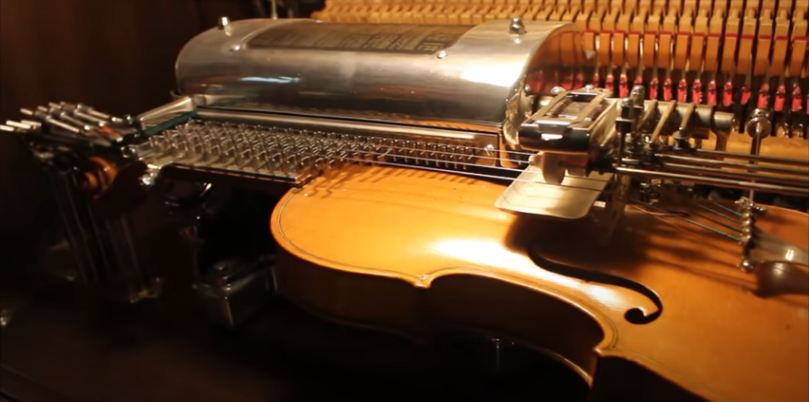 |
| Left: Mills Violano Virtuoso: 1911
The Mills Violina Virtuoso was operated electrically by solenoids rather than by compressed air or vacuum. See the Sandell patent above. There is more info on the Mills Company here.
|
 |
| Left: Mills Violano Virtuoso: photo 1968
A photograph of a Violano Virtuoso once in the Jim Hamilton collection; there is more information here.
This looks absolutely identical to the machine in the two colour photographs above, and it may be the same one.
|

AUTOMATIC BANJOS
Automatic pianos were fairly common, but automatically playing a violin was much more of a technical challenge. Naturally one wonders what other instruments were put to work. The banjo? You are joking! Oh, no you're not.
 |
| Left: Automatic banjo machines: 1900s
Encore Automatic banjos; the one on the right is original, while the one on the left is a replica built by the D C Ramey Piano Company.
Plucking a banjo is less complicated than bowing a violin. It was done with four steel hooks, one for each string. These were constrained to move in an elliptical path when activated by their pneumatics. (bellows)
You can hear the replica Encore Automatic Banjo playing "By the Light of the Silvery Moon" on YouTube The Ramey Encore Banjo is based on the original Encore Automatic Banjo made between 1897 and 1906. The replica was built in 1991, and was put up for sale. It is known if it was sold; the market for automatic banjos is probably not large.
|
 |
| Left: Double Automatic Banjo machine: 1900s
If one Automatic Banjo is good, two must be better. Duelling Banjos anyone?
(As in played in the film Deliverance)
|
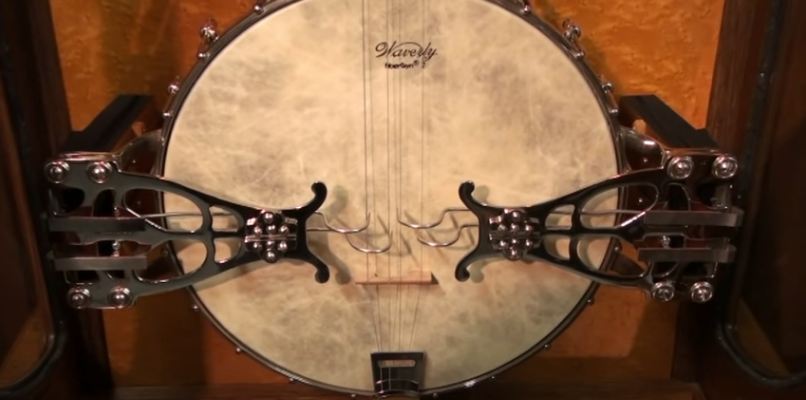 |
| Left: Automatic Banjo machine: 1900s
The rather scary-looking steel hooks that played the Automatic Banjos.
|
The Encore company later became that splendidly-named organisation, The American Automatic Banjo Company, Ltd. There is much information here.
Even more impressive was a complete banjo orchestra combining seven instruments: banjo, piano, snare-drum, bass-drum, triangle, tambourine, and castanets. More info here.
There is also a complete banjo orchestra machine to be heard on YouTube, playing 'Rock Around the Clock'. This version of the Banjo-Orchestra is composed of nine instruments: piano, banjo, snare drum, tambourine, triangle, wood block, castanets, bass drum, and cymbal. The instrument operates from a unique ten-tune orchestrated music roll. You can arrange to have one made for you by the D C Ramey Piano Company.The price is unknown.

OTHER MECHANICAL INSTRUMENTS
You may notice that the instruments in this section are not stringed instruments. They have a temporary home here while I plan separate galleries for Auromatic Brass and Automatic Woodwind.
THE AUTOMATIC TRUMPET
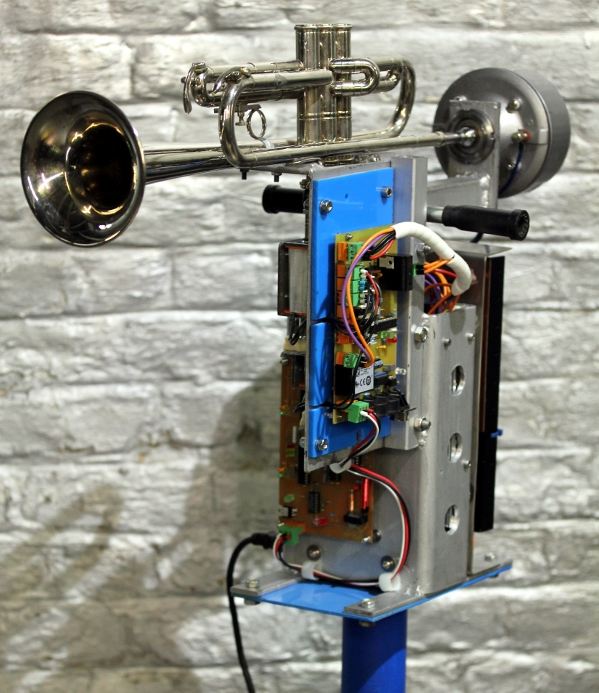 |
| Left: Automatic Trumpet: 2021
This is a robotic Bb trumpet designed and made to the order of the composer Alain Van Zeveren by Dr Godfried-Willem Raes. It is blown by a 75 Watt motor compressor horn driver and the valves are operated by 5V push solenoids. The trumpet is mounted upside down so that gravity assists the operation of the valves. The trumpet is driven by MIDI data applied to a PIC microcontroller, and:
"When a note is requested from the trumpet, the firmware will calculate the optimum valve combination- including non -rthodox fingerings- for the requested pitch. Thus a resonant standing wave in the instrument can be produced. Microtonal pitches are implemented such that the instrument is capable of performing quartertone music, as well as a wide range of different tunings and temperaments with great perfection."
Quoted from the link below:
|
There is a great deal of info on the Automatic Trumpet here. I am much impressed.
|

THE AUTOMATIC SAXOPHONE
 |
| Left: Automatic Alto Saxophone: 2013
This Automatic Alto Saxophone was built by Dr Godfried-Willem Raes, who built the Automatic Trumpet just above. The saxophone is 'blown' using a membrane compression driver followed by an acoustic impedance convertor. There are 18 solenoids that operate modified keywork. The Saxophone is controlled by MIDI data.
Solenoids also arrenged to move the whole saxophone assembly up and down, and left and right, as it would be with a human player.
There is much more Automatic Saxophone info here.
I am again much impressed; the Automatic Trumpet and the Automatic Saxophone merely scratch the surface of the number of automatic instruments he has made over many years. There is a chronological list running from 1964 to the present day here.
|
THE AUTOMATIC MARBLE INSTRUMENT
 |
| Left: The Marble Machine: 1900s
As an example of completely mad (but entirely praiseworthy) musical machinery, here is the Wintergatan Marble Music Machine on YouTube. It uses 2000 marbles.
It is quite brilliant.
Note the multiple funnels for catching the marbles bouncing off the xylophone plates.
|
THE TRIO FANTASTIQUE ROBOT JAZZ BAND
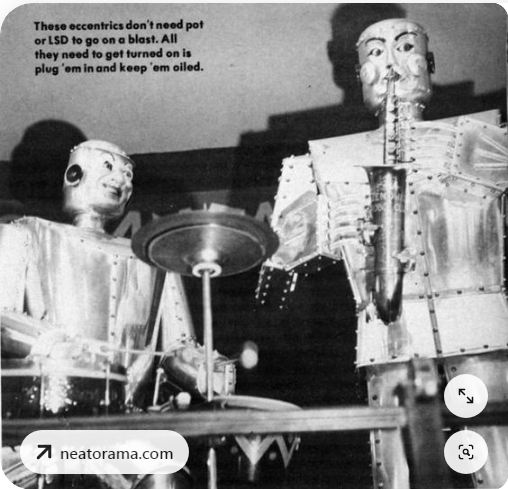 |
| Left: The Trio Fantastique Robot Band: 1954-59
This is a robot band called the Trio Fantastique, built by a Belgian engineer named Zenon Specht. The Trio Fantastique consisted of Wink on guitar, Blink on drums, and Nod on alto saxophone; they were the house band for Antwerp’s Robot Club, (a club regrettably unknown to Google) which was owned by Specht. They also made appearances in various fairs and departments stores around France between 1954 and 1959. Their repertoire was not limited to bebop but also included jazz, tangos and classical pieces.
Little is currently known about the technology but it seems to have used punched tape to control solenoids via relay decoding. How the saxophone was blown, and if it had the usual single-reed, is currently unknown.
The drummer seems to be a cheerful soul. Irritatingly so.
There's a six-second clip widely claimed to be of the band in action on YouTube, but I had my doubts, and the clip is actually of the Les Robots Music Band; see below. So far no video of The Trio Fantastique in action has been found; surely there must be some movie footage somewhere7 Can anyone help?
There is more info on the Trio Fantastique here, but the link given again shows the Les Robots Music Band.
Be aware there is human string/piano trio currently about which is also called The Trio Fantastique; this does not help with Google searches.
|
 |
| Left: The Trio Fantastique Robot Band: 1954-59
Note that the guitarist's left 'hand' is a big rectangular box presumably containing six solenoids to fret the strings.
There is a remarkable website is owned by the grandson of Zenon Specht. It has many pictures of The Trio Fantastique, spread over 5 pages.
|
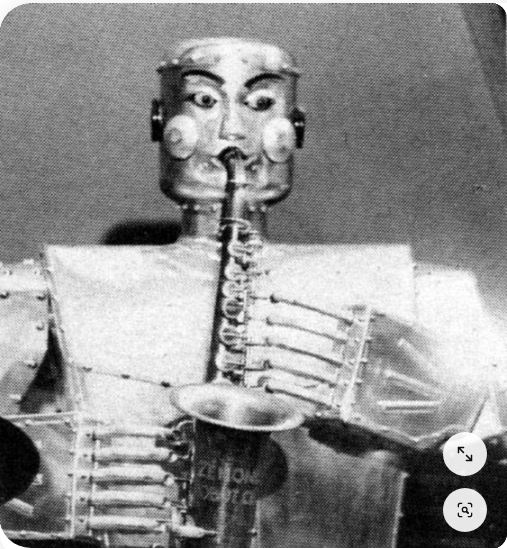 |
| Left: The Trio Fantastique Robot Band: 1954-59
The big five-fingered hands of the saxophonist.
You can just read the words 'ZENON' and 'ROBOT' on the bell of the saxophone. No doubt whose band this is.
But the question is: Is the saxophonist actually playing the instrument? It appears the saxophone sound of the Decap robor band (below) was actually produced by a Hammond electric organ behind the rear curtain of the stage, with loudspeakers either side of the performers. The problem is simulating the embouchure of a human player combined with a single-reed mouthpiece. I suspect a similiar fiddle (ha!) here, but the matter is currently uncertain.
|
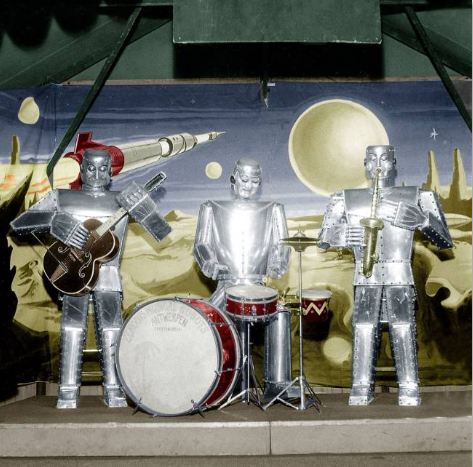 |
| Left: The Trio Fantastique Robot Band: 1959
Here are the chaps displayed at The Fair in Lens, France, in 1959. It looks as thought the saxophonist has the ability to close his eyes.
Note the six-fingered right 'hand' on the guitarist, one finger to pluck each string.
The image has at some point been colourised.
|
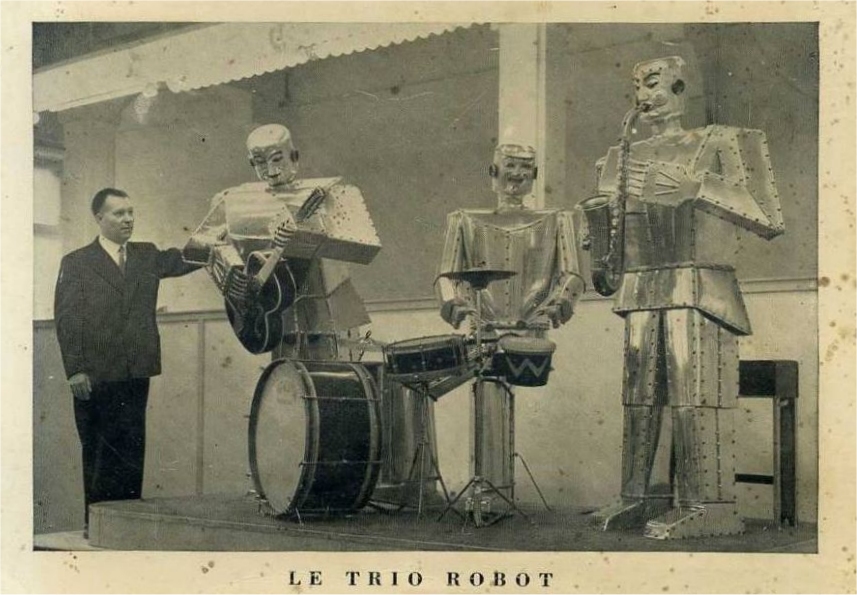 |
| Left: The Trio Fantastique Robot Band: 1959
That is presumably Zenon Specht at left.
What seems to be missing from all the pictures of the Trio Fantastique is the multicore electrical cable which surely must have been connnected to each robot. The cables were either very well hidden or removed before photography,
|
 |
| Left: Les Trio Fantastique Band: 1950s
The impressive cover of a literary review of 'strange fiction'. The price shows it is a French publication.
I for one welcome our new robot-musician overlords.
|
LES ROBOTS MUSIC BAND
 |
| Left: Les Robots Music Band: 1950s
This robotic band was built by Edouard Diomgar during the 1950s. As it says just under the title: "They play on real instruments". This is a record sleeve, but there is some doubt as to whether it's mono or stereo.
The trio play accordion, (Oskar) drums, (Ernest) and alto saxophone. (Anatole) The appearance of the robots is rather different from that of the Trio Fantastique. For a start they are all wearing crash helmets with rotating 'radar scanners' on top, and they all have big corrugated arms. The accordionist has a giant right hand to cover the keyboard, and is smoking a cigarette; actually, as smoke is puffed out during the performance.
There is a short clip of the band in action on YouTube The saxophonist has rubber cheeks that move in and out with the music and are very creepy indeed.
Note the non-French spelling of 'Music'.
|
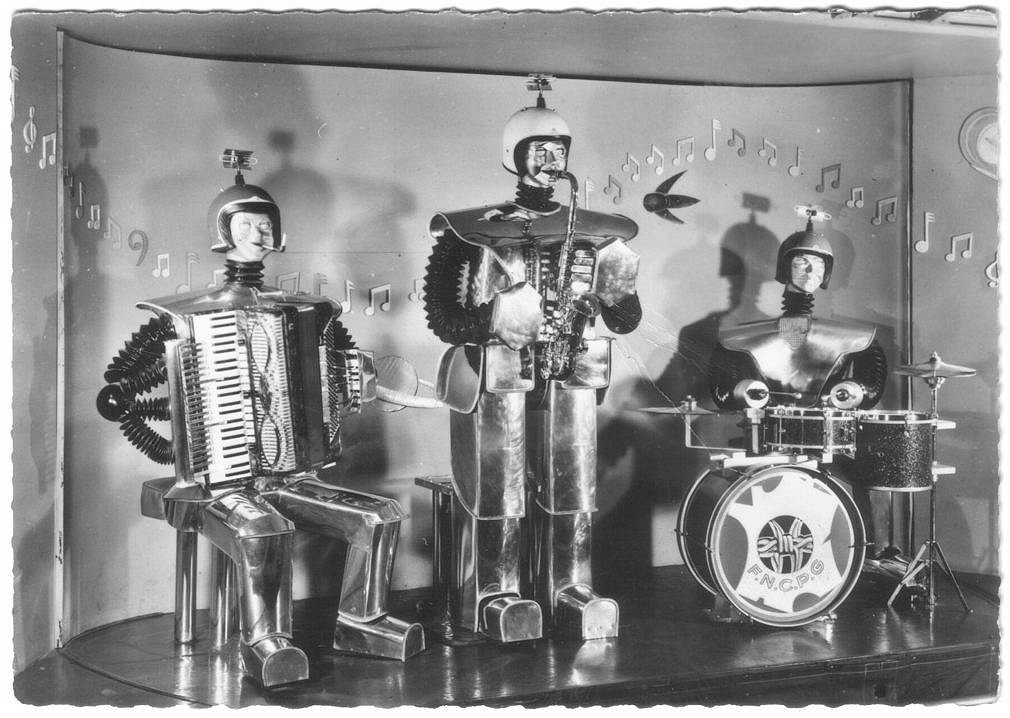 |
| Left: Les Robots Music Band: 1950s
Here you can see that the accordionist has three forearms.
There is also a rather longer clip of the band (38 seconds) on YouTube. During this performance the saxophonist stands up, moves his head, and then sits down again.
A thick cable can be seen running from the back of the stage to the right wrist of the sax player. This is the only robot band picture found so far where a control cable is visible.
There is more information here, and here, and also here.
|
THE DECAP ROBOT BANDS
 |
| Left: A Decap Band: 1950s
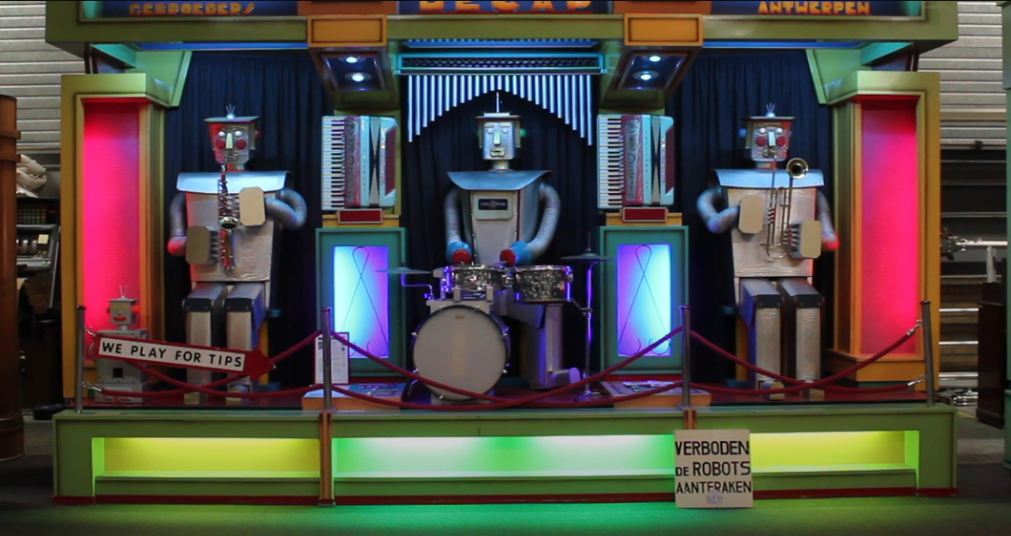
In the early 1950’s and 60's, Gebroeders Decap of Antwerp, Belgium built no less than seven sets of robot musicians. This the largest of them; it is a 105 key instrument built in 1963. Only three 105 key Decap organs were produced.
A C Pilmer have restored two of them.
Here we have a saxophonist and a drummer, and it looks very much as if the guy on the right is playing a Cimbasso, not an instrument you encounter every day. The two wind players can stand up and sit down, their metal shoulders heave unsettlingly, and their rubber cheeks blow in and out. There is more info here.
There are also two accordians either side of the drummer, played by concealed means; the keys move, and the accordian bellows move in and out. The coloured panels provide a light show. Note the tiny robot at extreme left behind the WE PLAY FOR TIPS sign. It is not known if this has any functionality.
The notice says it is forbidden to touch the robots.
|
You can hear this band on YouTube, hereThe video includes the punched card reader (at 0.49) that controls the robots; judging by the great number of pipes in view the working system seem to be pneumatic, much like a pianola.
 |
| Left: Another Decap Band: 1950s
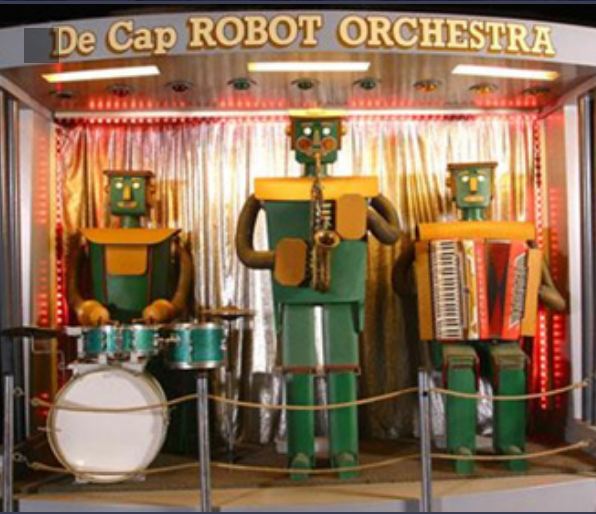
This is a smaller Decap robot band; the line-up this time is saxophone, drums, and accordian. The design of the robots looks exactly the same, though they are painted differently.
I have seen it stated in several places that the saxophone sound is actually produced by a Hammond electric organ behind the rear curtain of the stage, with loudspeakers either side of the performers. This seems highly plausible; I was wondering how the embouchure of a human sax player was replicated.
You can see and hear a similar Decap robot band on YouTube, but it is not the same one..
There is another similar but different Decap robot band on YouTube here.
And yet another similar but different Decap robot band on YouTube here, playing 'YMCA' by the Village People; obviously the art of cutting new punched cards has not been lost.
There is a very informative PDF here
|
 |
| Left: A Decap Band: 1950s
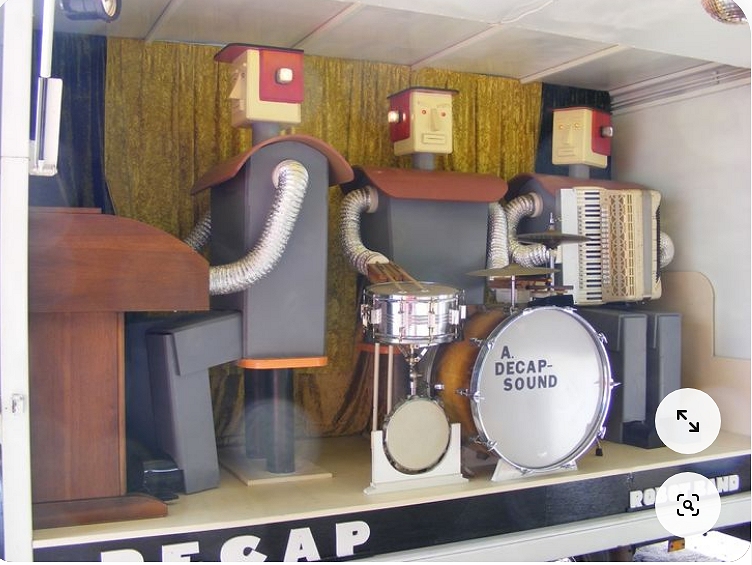
This is another Decap robot band; the line-up now is keyboards, drums, and accordian. The design of the robot heads is different from those above.
Note the tambourine to the left of the kick-drum; this is also played, apparently by the drummer. How the keyboard is played is not currently known.
You can see the set-up and hear this band on YouTube.
There is another Decap band on which gives close-ups of the accordian showing the 'fingers' that work the keys at around 1:50 into the video.
|
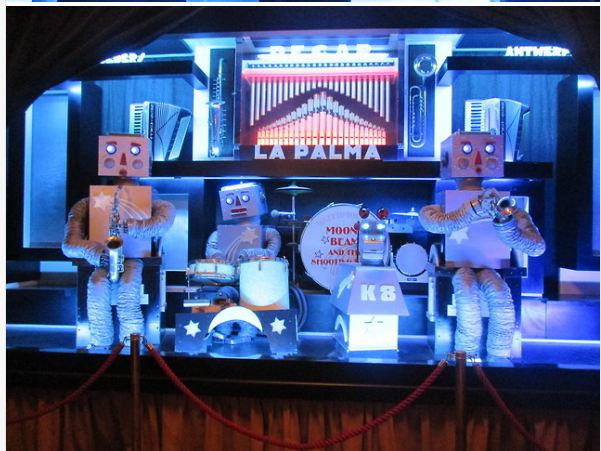 |
| Left: A Decap Band at Watermouth Castle: Moony Beam and the Shooting Stars: 19??
This Decap Band is one of the attractions at Watermouth Castle in Ilfracombe, Devon, England.
Note that this band includes a robot dog at centre right. It is marked K8, a reference to Doctor Who's K9, also a robot dog.
You can hear this band on YouTube.
|
MODERN ROBOT BANDS: COMPRESSORHEAD
 |
| Left: Compressorhead Robot Band: 2012
Building a robot band has recently been made rather simpler by the arrival of computers, microcontrollers, and MIDI, though it is of course still no light undertaking.
A modern robot band is Compressorhead, which initially consisted of 'Fingers' on lead guitar, 'Bones' on bass guitar, 'Stickboy' on drums, and 'Junior' a much smaller robot that plays hi-hat cymbal only. Stickboy has four arms, filling a long-felt want in the rhythym sections of bands, and two legs to work the kick-drum; why a four-armed drummer would need Junior as an assistant is not immediately clear; Junior can be spotted at bottom right.
These first four robots were built between 2007 and 2012. You can hear them playing a version of the Motorhead song 'Ace of Spades' on YouTube. Highly recommended!
Compressorhead have a Wikipedia page.
My deep respect to all concerned.
|
 |
| Left: Compressorhead Robot Band: 2017
In 2017, the band added a the vocalist robot Mega-Wattson (voiced by John Wright), and Hellgå Tarr, a second guitarist, who appears to be 'female'.
Here Mega-Wattson is in the foreground, mounted on some hefty caterpillar tracks, the base of which carries what is apparently some sort of laser cannon. 'Bones' on bass guitar is at the left, also on tracks. I think that's Hellgå Tarr, in the right background. 'Stickboy' is barely visible behind the drum kit.
This later incarnation (if that's the word) of Compressorhead with the 350 kgm Mega-Wattson on caterpillar tracks can be heard on YouTube.
|























































